Background process management is essential for maintaining optimal system performance. Efficient management of background processes can significantly enhance the speed and responsiveness of your computer. Many users overlook the impact that background processes have on their system’s efficiency. This article will delve into the importance of managing background processes, exploring popular tools that can help streamline this task.
Importance of Managing Background Processes
Managing background processes is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, background processes can consume a considerable amount of system resources, leading to decreased performance. By effectively managing these processes, users can ensure that their system operates smoothly and efficiently. Moreover, understanding which processes are running in the background can help identify unnecessary applications that may be slowing down the computer.
Here are key reasons why background process management is important:
- Improved System Performance: Reducing the number of active processes can lead to faster response times and overall improved performance.
- Enhanced Security: Monitoring background processes can help detect malicious software that may be running without the user’s knowledge.
- Better Resource Allocation: Understanding which applications consume the most resources allows users to allocate their system’s capabilities more effectively.
- Extended Hardware Lifespan: Efficient management can reduce wear and tear on hardware components, extending their lifespan.
In conclusion, managing background processes is not just about improving speed; it’s about creating a more secure and efficient computing environment. With the right tools, users can take control of their system and enhance its performance significantly.
Overview of Popular Tools
There are several tools available for background process management, each offering unique features and benefits. Understanding these tools can help users select the best one for their needs. Below is an overview of some of the most popular tools in the market:
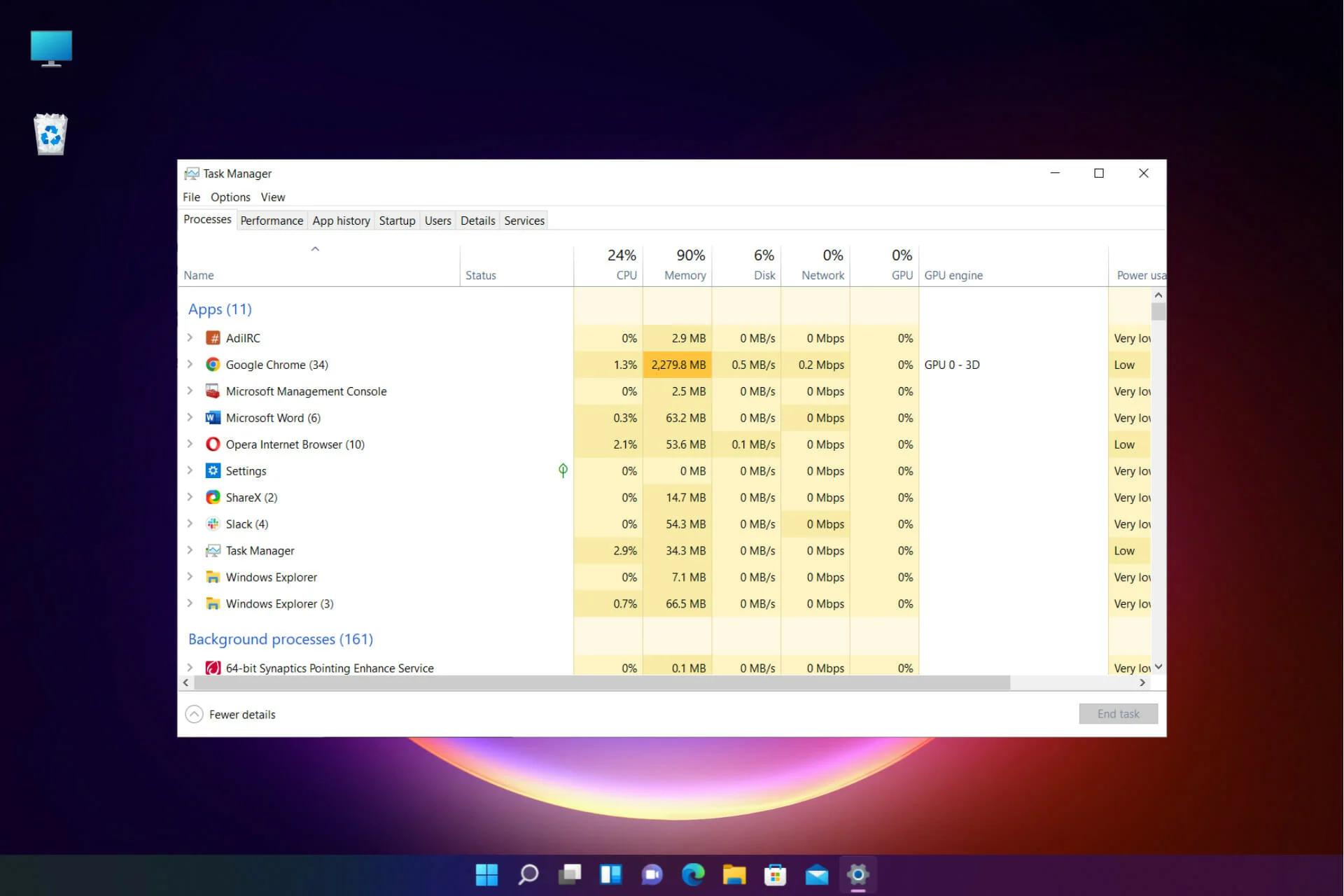
- Task Manager (Windows): A built-in utility that provides real-time information about background processes, CPU usage, and memory consumption. It allows users to end tasks and monitor performance easily.
- Process Explorer: A more advanced tool from Microsoft that offers detailed information about system processes. It provides insights into process hierarchies and resource usage, making it easier to identify problematic applications.
- CCleaner: While primarily known for system cleanup, CCleaner also includes features for managing startup programs and background processes, ensuring that only essential applications run.
- System Explorer: This free tool offers a comprehensive view of running processes, allowing users to analyze and manage them effectively. It includes additional features like a process history and online security checks.
- Autoruns: Another Microsoft tool that focuses on startup processes. It helps users manage which applications launch on startup, reducing boot time and resource consumption.
Choosing the right tool for background process management can greatly enhance a user’s ability to monitor and control system performance. By utilizing these tools, individuals can make informed decisions about which processes to keep active and which to terminate.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Each Tool
Background process management can be daunting, but with the right tools and guidance, it becomes manageable. Below is a step-by-step guide to using some of the most popular tools for managing background processes effectively.
1. Using Task Manager
Task Manager is a built-in utility in Windows that provides an overview of running applications and processes. To access it, right-click on the taskbar and select “Task Manager” or press Ctrl + Shift + Esc.
- Once open, navigate to the “Processes” tab to see a list of active applications and background processes.
- Right-click on any process to view options such as “End Task” or “Open File Location”.
- Monitor CPU and memory usage to identify processes consuming excessive resources.
Using Task Manager allows users to terminate unresponsive applications quickly and manage startup programs efficiently.
2. Utilizing Process Explorer
Process Explorer offers advanced features for background process management. Download it from the official Microsoft website and run the executable file.
- Upon launching, you’ll see a detailed tree view of all processes running on your system.
- Hover over a process to view additional information, such as the process’s path and its resource usage.
- Right-click on any process to suspend or terminate it, or to check its properties for further analysis.
Process Explorer provides a more comprehensive insight into background processes compared to Task Manager, making it easier to identify problematic applications.
3. Cleaning Up with CCleaner
CCleaner is known for its cleaning capabilities, but it also features tools for managing background processes. Download CCleaner and install it on your system.
- Open CCleaner and navigate to the “Tools” section.
- Select “Startup” to view applications that launch at startup.
- Disable or remove unnecessary applications to improve boot time and overall system performance.
By using CCleaner, users can not only clean up their system but also streamline the startup process, enhancing background process management.
4. Analyzing with System Explorer
System Explorer is a free tool that provides detailed information about running processes. Download it and launch the application to begin.
- Navigate to the “Processes” tab to view all active processes along with their CPU and memory usage.
- Right-click on a process to access options such as “Kill Process” or “Search Online” for more information.
- Utilize the “Startup” tab to manage startup programs effectively.
System Explorer enhances the user’s ability to manage background processes by offering additional resources and options for each process.
5. Managing Startup with Autoruns
Autoruns is a powerful tool from Microsoft that allows users to manage startup processes comprehensively. Download and run Autoruns to begin.
- Upon opening, Autoruns displays all applications set to run at startup, including background processes.
- Review the list and uncheck any unnecessary applications to prevent them from starting automatically.
- Use the “Logon” tab to specifically manage processes that launch during user logon.
Autoruns helps users streamline their startup processes significantly, aiding in effective background process management.
Comparing Features of Top Tools
When considering background process management, comparing the features of various tools is essential for selecting the right one. Below is a comparison of the top tools mentioned earlier.
Task Manager vs. Process Explorer
- Task Manager: Basic overview of running processes, user-friendly interface, limited details on process hierarchies.
- Process Explorer: Advanced insights into processes, detailed information on resource usage, ability to suspend processes.
CCleaner vs. System Explorer
- CCleaner: Primarily a cleaning tool, includes basic process management, focuses on startup applications.
- System Explorer: Comprehensive process analysis, additional features like process history and online checks, better for detailed monitoring.
Autoruns vs. Other Tools
- Autoruns: Focuses solely on startup applications, extensive control over background processes that launch at startup.
- Other Tools: May provide limited startup management features compared to Autoruns.
Choosing the right tool for background process management depends on individual needs. For users looking for comprehensive insights, Process Explorer and System Explorer are excellent choices. For cleaning and startup management, CCleaner and Autoruns are recommended.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Background process management can sometimes lead to unexpected issues. Identifying and troubleshooting these problems is essential for maintaining system performance. Common issues include high CPU usage, unresponsive applications, and slow boot times. Understanding these challenges can help users take effective action.
High CPU Usage
High CPU usage is one of the most common problems associated with background processes. When certain applications or processes consume excessive CPU resources, it can lead to system sluggishness. To troubleshoot this issue:
- Open Task Manager and navigate to the “Processes” tab.
- Sort processes by CPU usage to identify the culprits.
- Terminate any unnecessary processes that are consuming too much CPU.
- If a specific application consistently uses high CPU, consider reinstalling it or checking for updates.
Regularly monitoring CPU usage can help prevent this issue from becoming a recurring problem.
Unresponsive Applications
Sometimes, applications may become unresponsive due to background processes interfering with their operation. If this occurs, users can follow these steps:
- Use Task Manager to end the unresponsive application.
- Check for any background processes that might be hogging system resources.
- Restart the computer to refresh the system state.
- Consider increasing system memory or upgrading hardware if unresponsiveness persists.
Understanding the relationship between background processes and application performance is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
Slow Boot Times
Slow boot times can be frustrating and are often caused by too many applications launching at startup. To address this issue:
- Utilize Autoruns to manage startup applications.
- Uncheck any unnecessary applications to reduce the startup load.
- Regularly clean up temporary files using tools like CCleaner.
- Consider upgrading to an SSD if the boot time is excessively slow.
By managing startup processes effectively, users can significantly improve boot times and overall system performance.
Conclusion and Best Practices
Effective background process management is vital for maintaining optimal system performance. Understanding how to monitor and control background processes can lead to a smoother computing experience. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Regularly check for unnecessary background processes using Task Manager or Process Explorer.
- Manage startup applications with Autoruns to enhance boot times.
- Utilize system cleanup tools like CCleaner to keep the system free from clutter.
- Stay updated on software versions to prevent compatibility issues.
- Educate yourself about which processes are essential and which can be terminated.
By implementing these best practices, users can ensure their systems run efficiently and effectively. Proper background process management not only enhances performance but also improves security and user experience. For further learning, consider exploring resources such as the Microsoft documentation and technology forums that provide insights into system optimization.