This article covers the differences between Apple partition types, specifically HFS+ and APFS. It explains their advantages and disadvantages, compatibility with macOS versions, and provides guidance on creating and configuring partitions. It also addresses how to change partition types without data loss and when to choose one over the other based on user needs and common scenarios.
Overview of Apple Partition Types
Apple partition types are crucial for managing storage on Mac systems. Understanding these types is vital for users who want to optimize their devices. The most common partition types are HFS+ and APFS. Each serves different purposes and is tailored for specific use cases.
HFS+ (Hierarchical File System Plus) has been the standard for many years. It supports features like journaling, which helps prevent data corruption. However, with the introduction of APFS (Apple File System), Apple moved towards a more modern approach, enhancing performance and security.
APFS is designed for solid-state drives (SSDs) and offers improved speed and efficiency. It includes features like space sharing, cloning for files and directories, and snapshots, which are essential for backup purposes.
In summary, knowing the differences between these partition types helps users choose the right one for their needs. Whether you are an everyday user or a tech enthusiast, understanding Apple partition types is essential for effective storage management.
Difference between HFS+ and APFS
The difference between HFS+ and APFS is significant. While HFS+ has served well for traditional hard drives, APFS is optimized for SSDs. This optimization leads to faster file access and overall improved system performance.
One key difference is how each system handles data. HFS+ uses a block-based approach, which can slow down performance as the drive fills up. On the other hand, APFS uses a more efficient allocation method that allows for quicker read and write operations.
Another notable difference is in security features. APFS provides stronger encryption options, allowing for better protection of sensitive data. It also supports multiple encryption keys for different files, enhancing security.
In terms of compatibility, HFS+ works with older versions of macOS, while APFS is compatible with macOS High Sierra and later. This means that users with older systems may need to stick with HFS+ unless they upgrade their operating systems.
Overall, understanding these differences helps users make informed decisions about their partition types based on performance, security, and compatibility.
Advantages and Disadvantages of HFS+ and APFS
When considering the advantages and disadvantages of HFS+ and APFS, it’s essential to weigh their features against user needs.
- Advantages of HFS+:
- Compatibility with older macOS versions.
- Proven reliability over the years.
- Supports journaling for data integrity.
- Disadvantages of HFS+:
- Slower performance on SSDs compared to APFS.
- Limited modern features like snapshots and cloning.
- Advantages of APFS:
- Optimized for SSDs, resulting in faster performance.
- Supports advanced features like cloning and snapshots.
- Enhanced security with strong encryption methods.
- Disadvantages of APFS:
- Not compatible with older macOS versions.
- May have issues when used with traditional hard drives.
Ultimately, the choice between HFS+ and APFS depends on individual needs, such as hardware compatibility and performance expectations.
When to Use APFS Instead of HFS+
Choosing APFS over HFS+ depends on specific scenarios and user needs. Here are some guidelines to help you decide:
- Solid-State Drives (SSDs): If your Mac uses an SSD, APFS is the clear winner. It’s optimized for flash storage, providing faster read and write speeds.
- Performance Requirements: For users who need quick access to files and applications, APFS delivers superior performance, particularly when dealing with large files or databases.
- Backup Needs: If you frequently use Time Machine or require snapshots for backups, APFS is beneficial. Its snapshot feature allows for efficient backups and recovery.
- Encryption Needs: If you prioritize security, APFS offers advanced encryption options, making it ideal for storing sensitive information.
- Compatibility Considerations: Keep in mind that APFS is compatible only with macOS High Sierra and later. If you’re using an older macOS version, HFS+ may still be necessary.
In summary, use APFS when working with SSDs, needing high performance, utilizing backups, or requiring strong encryption. For older systems or traditional hard drives, HFS+ may still serve you well.
Compatibility of Partition Types with macOS Versions
Understanding the compatibility of partition types with macOS versions is essential for effective storage management. Here’s a breakdown:
- HFS+: This partition type works seamlessly with older versions of macOS, including macOS Sierra and earlier. It remains a reliable choice for users who haven’t upgraded their systems.
- APFS: Introduced with macOS High Sierra, APFS is designed specifically for SSDs and is not backward compatible with older macOS versions. Users must upgrade to at least High Sierra to utilize APFS.
In essence, if you’re using macOS High Sierra or later, APFS is your go-to option. However, if you’re on an older version, HFS+ is your best bet.
Creating and Configuring Partitions on Mac
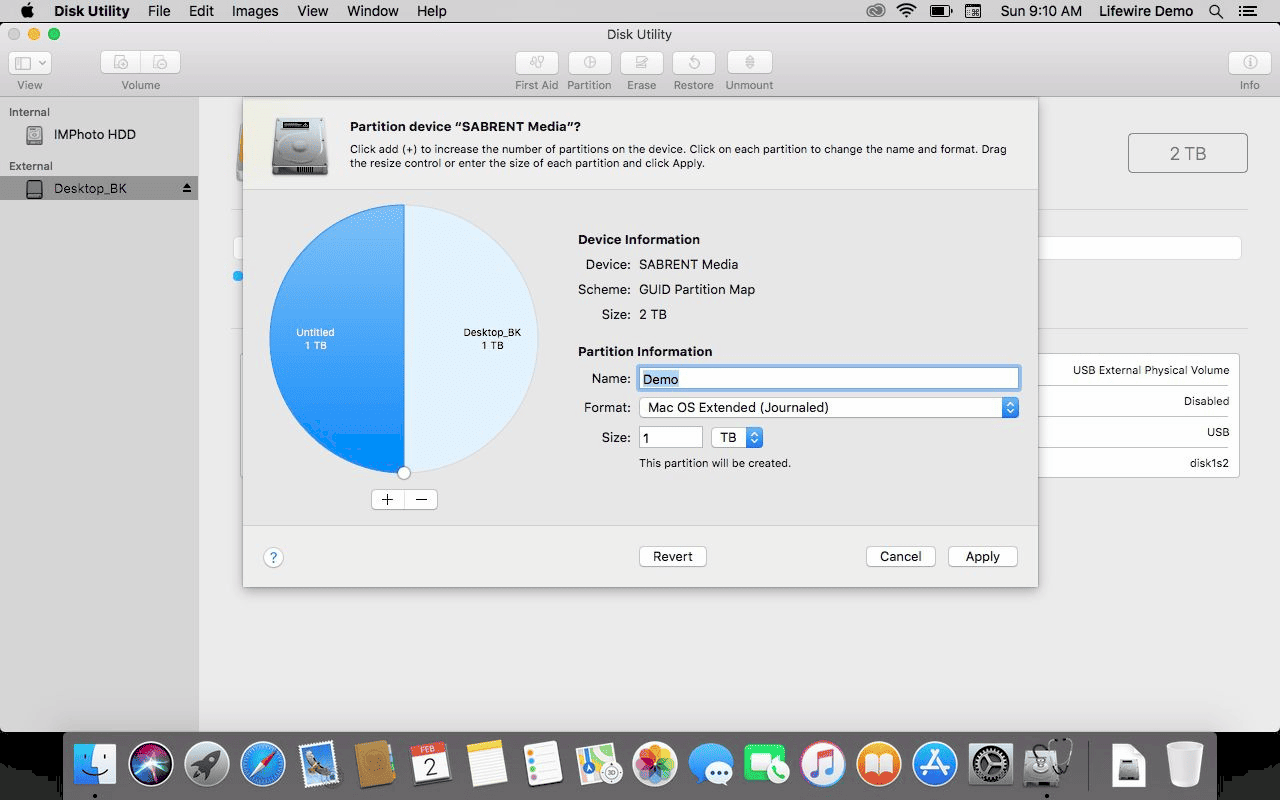
Creating and configuring partitions on a Mac is straightforward and can enhance your storage management. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Open Disk Utility: You can find this in Applications > Utilities. This tool allows you to manage your disks and partitions.
- Select Your Drive: In Disk Utility, choose the drive you wish to partition. Make sure to select the correct one to avoid data loss.
- Click on Partition: Click the “Partition” button to access the partitioning options.
- Add a Partition: Click the plus (+) button to create a new partition. Specify the size and format (HFS+ or APFS) based on your needs.
- Name Your Partition: Give your new partition a name that reflects its purpose, making it easier to identify later.
- Apply Changes: Click “Apply” to save your changes. Disk Utility will create the partition, which may take some time depending on the size.
Partitioning your Mac can help you organize files better, manage backups, and optimize storage. Always ensure that you back up your data before making changes to avoid accidental loss.
Changing Partition Type Without Data Loss
Changing the partition type without data loss is a crucial concern for many Mac users. Fortunately, there are methods to achieve this safely, ensuring that your data remains intact. Here are some approaches to consider:
- Backup Your Data: Always start by creating a complete backup of your important files. Use Time Machine or another backup solution to secure your data before making any changes.
- Using Disk Utility: Disk Utility is a built-in tool on macOS that allows you to modify partitions. You can format a partition to APFS or HFS+ without losing data if done correctly. Choose the partition, select “Erase,” and then choose the new format. However, ensure that the partition is not your startup disk.
- Third-Party Software: There are various third-party applications like Paragon Hard Disk Manager or Stellar Partition Manager that enable users to change partition types while preserving data. These tools often provide a user-friendly interface and additional functionalities.
- Terminal Commands: For advanced users, the Terminal can be used to change partition types. Commands like “diskutil” allow you to manipulate partitions effectively. However, this method requires a good understanding of command-line operations.
In conclusion, while changing the partition type without data loss is possible, it is essential to proceed with caution. Always back up your data first and choose the method that best suits your comfort level and technical expertise.
Choosing the Right Partition Type for Your Needs
Choosing the right partition type is vital for optimizing your Mac’s performance. Factors such as hardware compatibility, intended use, and performance requirements should guide your decision. Here’s how to make the right choice:
- Assess Your Hardware: If your Mac is equipped with an SSD, APFS is recommended due to its optimization for flash storage. For traditional hard drives, HFS+ remains a reliable option.
- Consider Your Usage: If you frequently work with large files or require high-speed access, APFS provides superior performance. On the other hand, if your tasks involve older applications or compatibility with legacy systems, HFS+ may be more suitable.
- Backup Requirements: If you utilize Time Machine for backups, APFS is advantageous due to its snapshot feature. This allows for more efficient backups and recovery processes.
- Security Needs: If data security is a priority, APFS offers better encryption options. This is essential for users storing sensitive information.
Ultimately, the choice between HFS+ and APFS should align with your specific needs and the capabilities of your Mac. Evaluating these factors will help ensure optimal performance and data safety.
Common Scenarios for Each Partition Type
Understanding common scenarios for HFS+ and APFS can help users select the appropriate partition type for their specific needs. Each format has its strengths and weaknesses depending on the use case:
- HFS+: Ideal for Older Systems: Users with legacy applications or older Macs will find HFS+ compatible and reliable. It is also suitable for external drives used with older macOS versions.
- APFS: Best for SSDs: For Macs equipped with SSDs, APFS is the go-to choice. It enhances performance, supports modern features, and is perfect for users who need quick file access.
- Mixed Use Cases: If you use both SSDs and traditional hard drives, consider partitioning your SSD with APFS and your hard drive with HFS+. This optimizes performance based on the storage type.
- Backup Scenarios: When using Time Machine for backups, APFS offers advantages like snapshots, making it easier to manage backup versions without significant performance hits.
By understanding these scenarios, users can make informed decisions about which partition type to use, ensuring they meet their specific storage needs effectively.